|
FreeRDP
|
Functions | |
| The Primitives Library Introduction The purpose of the primitives library is to give the freerdp code easy access to *run time *optimization via SIMD operations When the library is dynamic checks of processor features are | run (such as the support of SSE3 or Neon) |
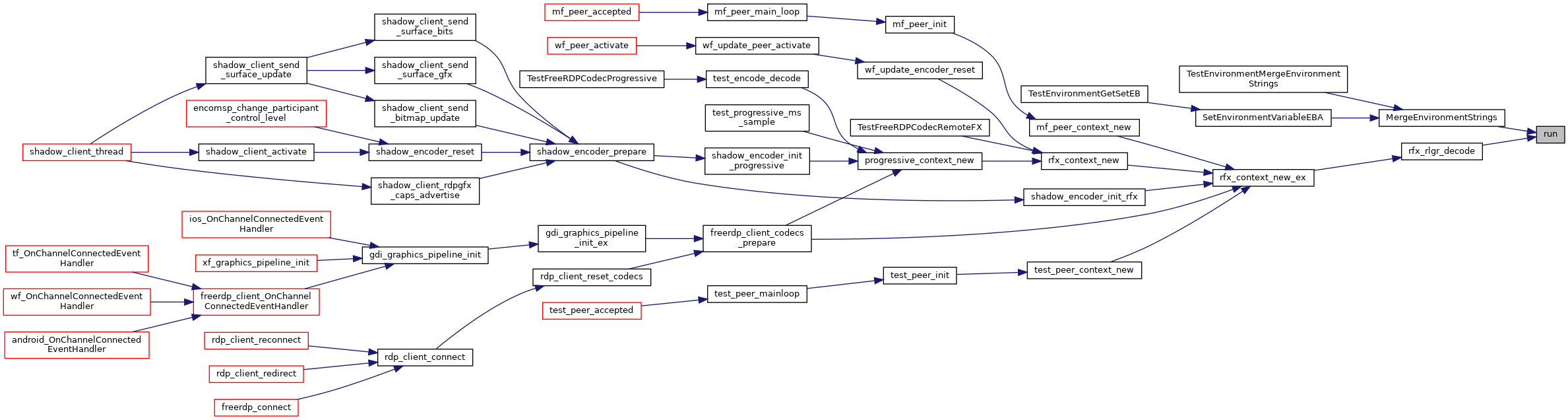
| The Primitives Library Introduction The purpose of the primitives library is to give the freerdp code easy access to *run time *optimization via SIMD operations When the library is dynamic checks of processor features are and entrypoints are linked to through function pointers to provide the fastest possible operations All routines offer generic C alternatives as fallbacks Run time optimization has the advantage of allowing a single executable to run fast on multiple platforms with different SIMD capabilities Use In Code A singleton pointing to a structure containing the function pointers is accessed through | primitives_get (). The function pointers can then be used from that structure |
| prims | shiftC_16s (buffer, shifts, buffer, 256) |
Variables | |
| The Primitives Library Introduction The purpose of the primitives library is to give the freerdp code easy access to *run time *optimization via SIMD operations When the library is | initialized |
| The Primitives Library Introduction The purpose of the primitives library is to give the freerdp code easy access to *run time *optimization via SIMD operations When the library is dynamic checks of processor features are and entrypoints are linked to through function pointers to provide the fastest possible operations All routines offer generic C alternatives as fallbacks Run time optimization has the advantage of allowing a single executable to run fast on multiple platforms with different SIMD capabilities Use In Code A singleton pointing to a structure containing the function pointers is accessed through e g primitives_t * | prims = primitives_get() |
| Of | course |
| Of there is some overhead in calling through the function pointer and setting up the SIMD | operations |
| Of there is some overhead in calling through the function pointer and setting up the SIMD so it would be counterproductive to call the primitives library for very small | operation |
| The Primitives Library Introduction The purpose of the primitives library is to give the freerdp code easy access to* run time* optimization via SIMD operations When the library is dynamic checks of processor features are and entrypoints are linked to through function pointers to provide the fastest possible operations All routines offer generic C alternatives as fallbacks Run time optimization has the advantage of allowing a single executable to run fast on multiple platforms with different SIMD capabilities Use In Code A singleton pointing to a structure containing the function pointers is accessed through primitives_get | ( | ) |
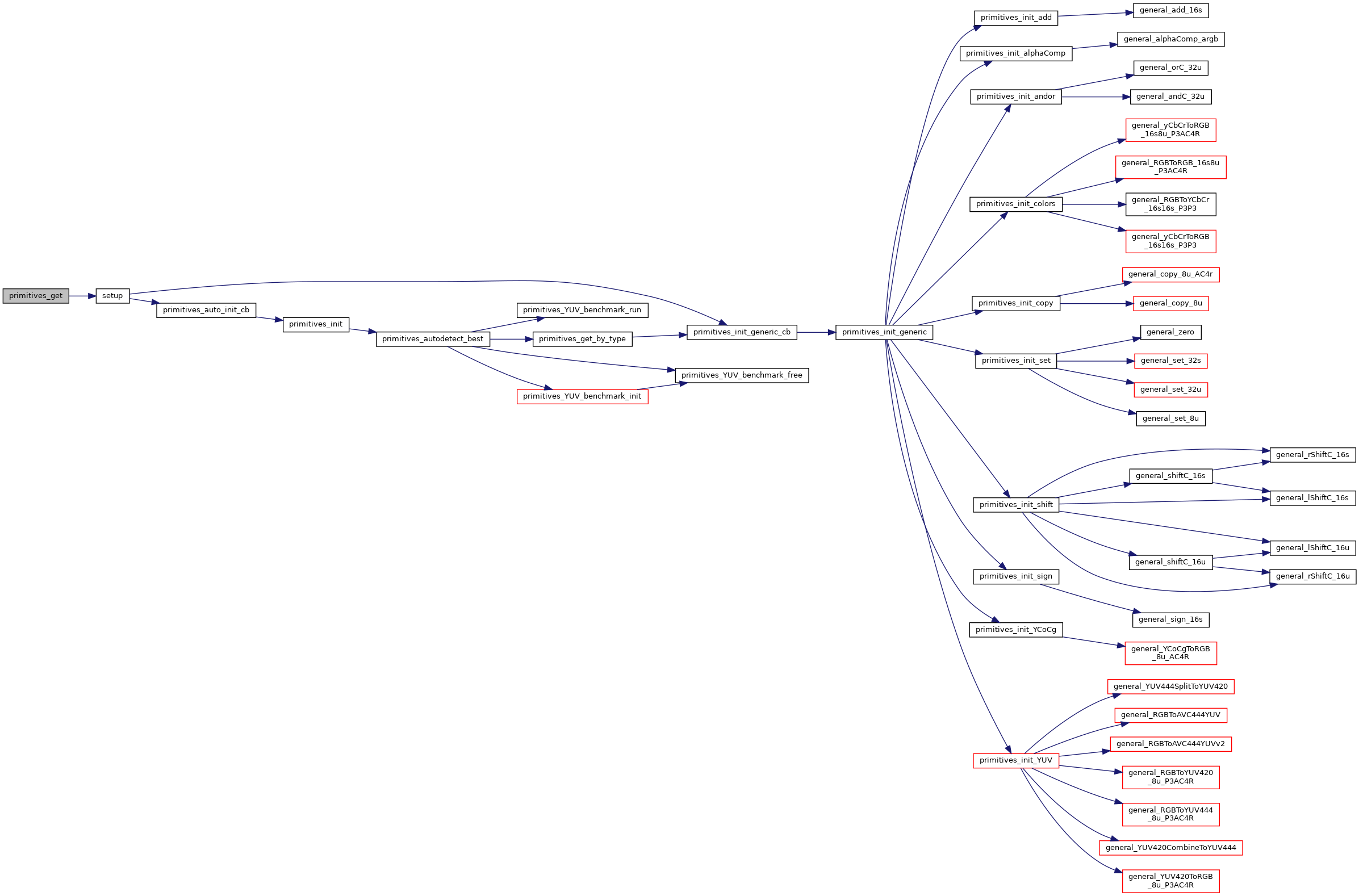
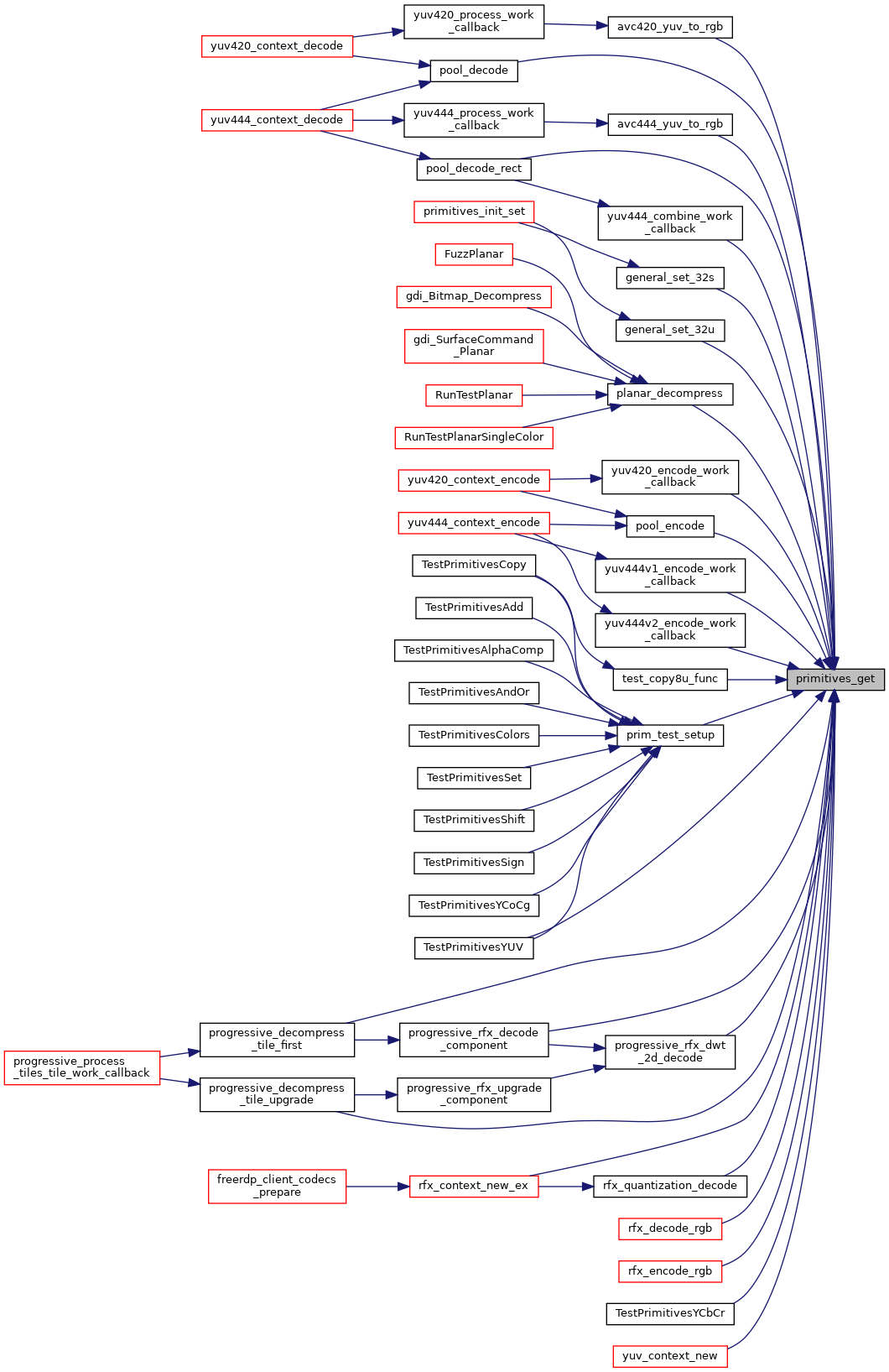
| The Primitives Library Introduction The purpose of the primitives library is to give the freerdp code easy access to* run time* optimization via SIMD operations When the library is dynamic checks of processor features are run | ( | such as the support of SSE3 or | Neon | ) |
| prims shiftC_16s | ( | buffer | , |
| shifts | , | ||
| buffer | , | ||
| 256 | |||
| ) |
| Of course |
| The Primitives Library Introduction The purpose of the primitives library is to give the freerdp code easy access to* run time* optimization via SIMD operations When the library is initialized |
| Of there is some overhead in calling through the function pointer and setting up the SIMD so it would be counterproductive to call the primitives library for very small operation |
| Of there is some overhead in calling through the function pointer and setting up the SIMD so it would be counterproductive to call the primitives library for very small e g initializing an array of eight values to a constant The primitives library is intended for larger scale operations |
| The Primitives Library Introduction The purpose of the primitives library is to give the freerdp code easy access to* run time* optimization via SIMD operations When the library is dynamic checks of processor features are and entrypoints are linked to through function pointers to provide the fastest possible operations All routines offer generic C alternatives as fallbacks Run time optimization has the advantage of allowing a single executable to run fast on multiple platforms with different SIMD capabilities Use In Code A singleton pointing to a structure containing the function pointers is accessed through e g primitives_t* prims = primitives_get() |